The database management system is a collection of data which allows users to perform many operations on the data. It connects with the users and other functions to catch and find out the data.
DBMS include three things
- End User
- Administration
- Designers
Objectives of DBMS - Data connection - Connection means which types of data user want it to keep to help the user provide all facilities. Data connection depends on two main things: cost performance and queries.
- Data integrity - Data integrity gives the trust safety for the reality of the database made by the user and controls the nature of the database.
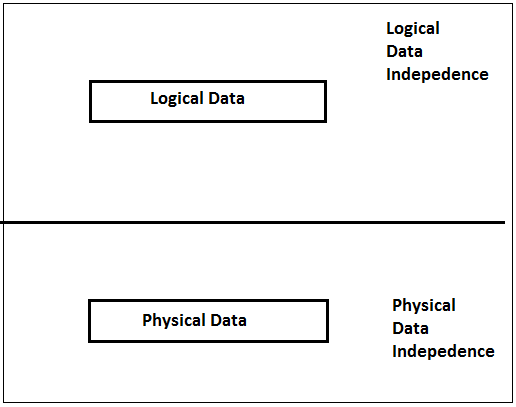
- Data Autonomy - This objective of DBMS provides the facility for the user use data independently. DBMS provides two types of data autonomy. The first one is physical data program, and the second is the logical data program, physical data programs which remains unaffected from the changes in the storage structure or access method, and the logical data program remains unaffected from the changes in the schema.
- Shareability - It allows sharing the data resources of the user and is a vital objective of database management. It keep help the user for making a database. Such as:
a. With the help of shareability we control common data which is views by different users.
b. We also join the parallel data. This is most helpful for the user because by this user search data easily.
c. Controlling concurrent updates so as to maintain the data integrity.
Instance of DBMS
Instance is the item stored in the database at a particular time, it is taking the current position of the data. Many instances can be constructed to compare to a fixed database schema. When we change the instance every time the database is updated it is also called a database state. It depends on the time.
Following are the concepts of instance:
- Relation instances - A relational database instance is a collection of table’s with their values at a define position. A Relational database instance is collection of instances which is a Table in a database.
- Tuples- A tuple separately identifies a unit. It is based on a fusion of attribute that consist of an attribute.
- Attribute Values - Attribute is a concept of an object or an entity.
- Entity- An entity is a real world thing. It depends on physical existence or conceptual existence.
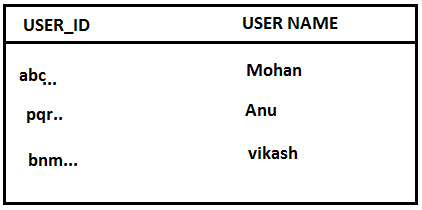
Example
Features of a DBMS
We have some common features of DBMS
- We can easily create, add and update data with the data structure.
- DBMS maintain large data.
- This is Query language.
- It provides the Reporting facility of the user.
- Security, Control, Backup and Rough Recovery.